HOW TO USE PPTP VPN ON ANDROID
PPTP VPN is one of the VPN protocols that already exists on every Android device of any brand and type. So it does not require additional applications to use it. Please click the first step until it is finished in a sequential manner to find out how to use pptp vpn (point to point tunneling protocol) on android devices.
The first step to using pptp vpn on android is to go directly to settings on android. Then select the add VPN menu. Every android device, whatever the brand, there must be a menu in the settings for VPN. for more details can be seen in the following image
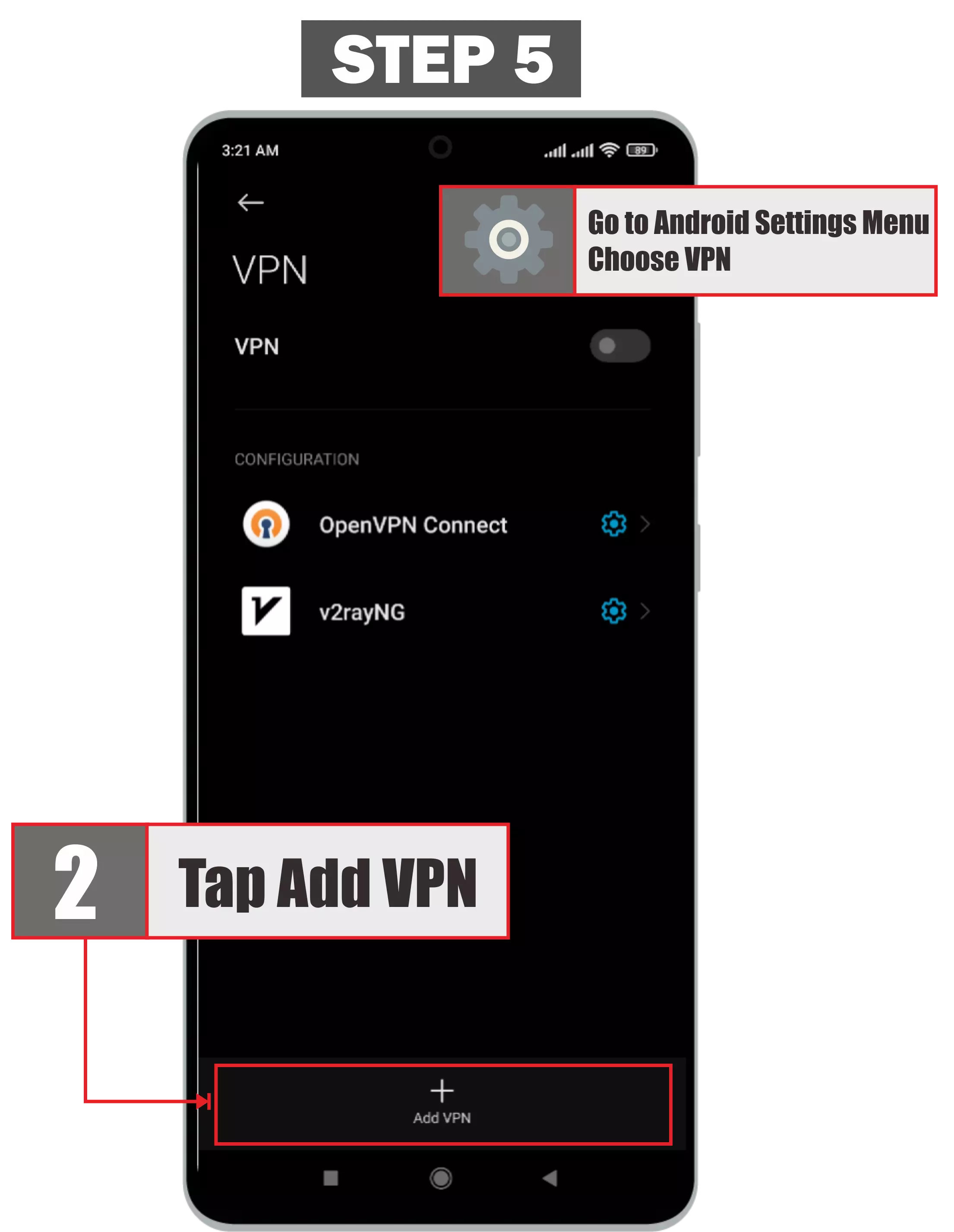
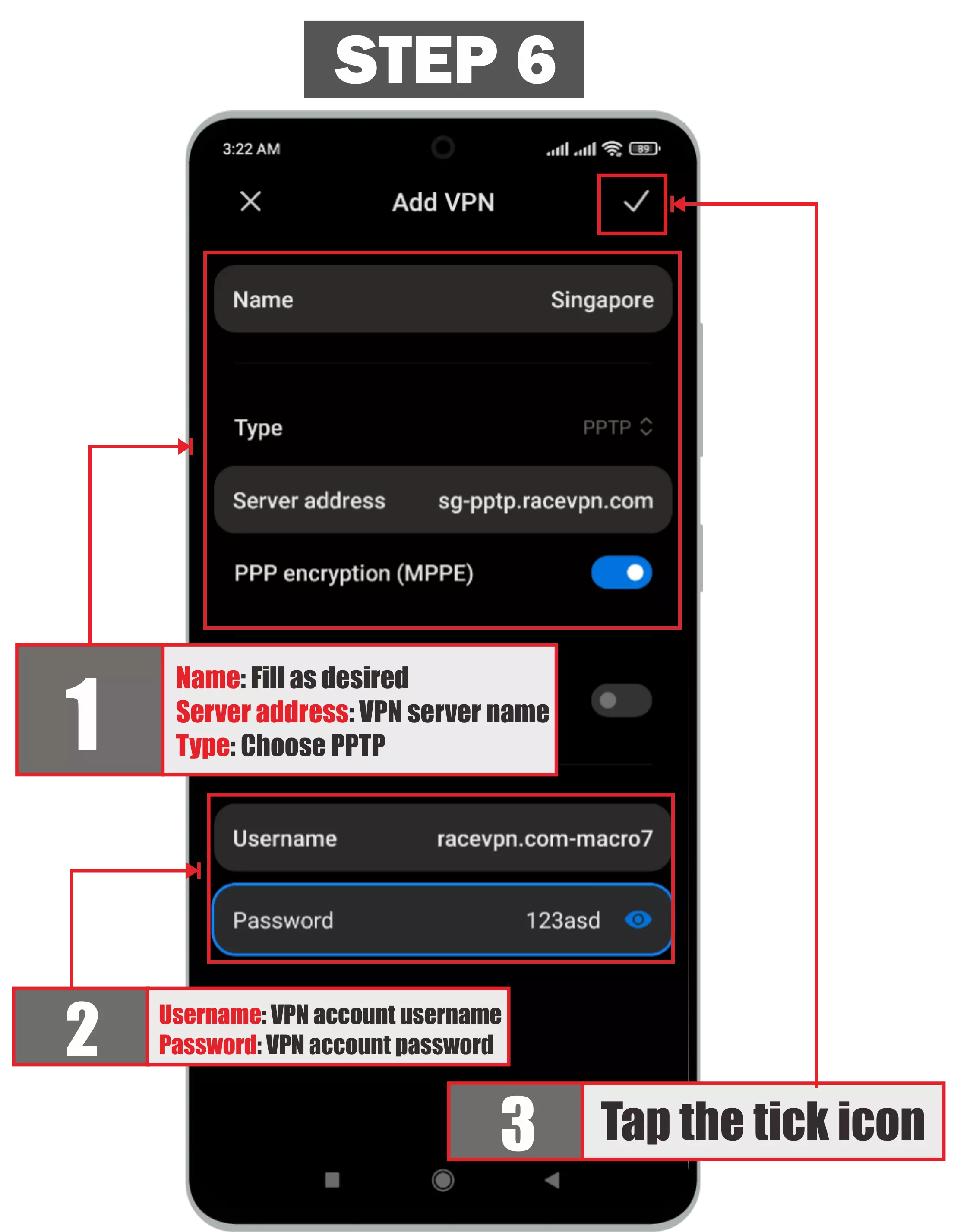
The next step is to fill in the name of the VPN that will be added to the android device (can be filled with any name). Then select the type / type of VPN you want to use. In the VPN type option, you will see many options. Select PPTP. Then in the server address column you can fill in the host server or ip server pptp vpn that you get. Then enter the username and password that you have obtained. And click the save button or ok. For more details, see this picture
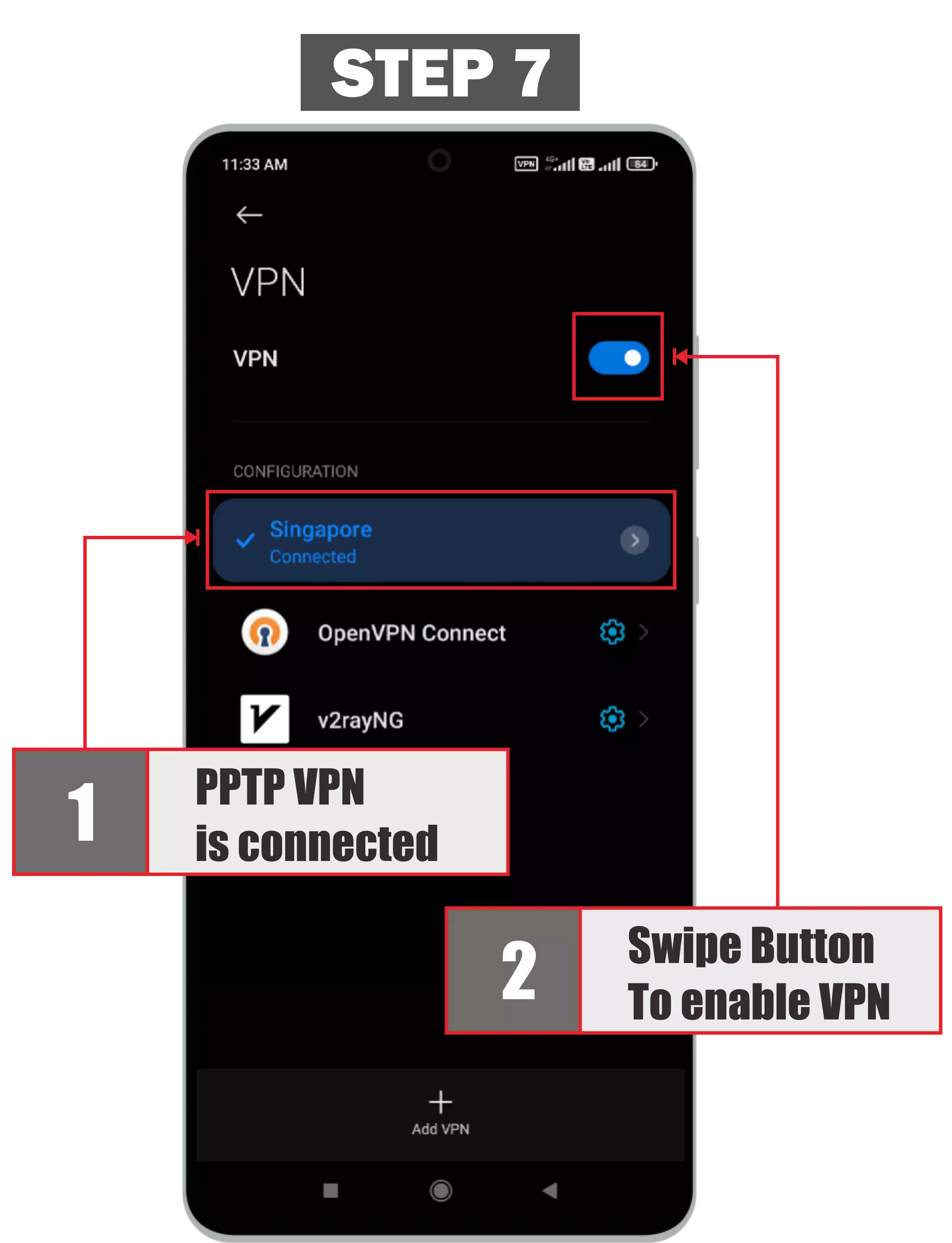
The last step is to make sure the VPN button is enabled (active) then click the VPN profile that you created as in the previous step and then select Connect. If unable to connect. Try again pressing the connect button. If you still can't connect, try restarting your Android device and then reconnecting. If it still doesn't connect you can try on another pptp vpn server or contact the admin to check the pptp vpn server
Why do you need vpn ?
Nothing is really safe when you enter the world of the internet, regardless of whether all our activities on the....
How does vpn work ?
The way the VPN itself works is by creating a network within the network (often called tunneling). Tunneling aims to.....
How to use vpn ?
Some internet users are still very new to the use of vpn, v2ray, vmess websocket, vless websockets, shadowsocks or.....
